Cover photo by Henri Pham. 4 minute read.
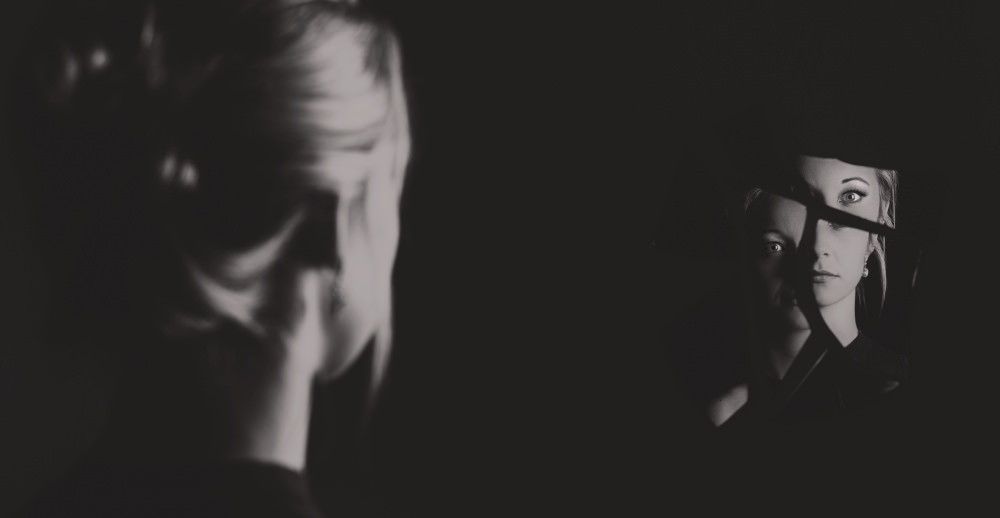
Did you know that porn can hurt your mental health, including distorting people’s perceptions of sex, intimacy, body image, and sexual performance?
Research indicates that consuming porn is linked with more negative body image, lower self-esteem, and poorer mental health.Owens, E. W., Behun, R. J., Manning, J. C., & Reid, R. C. (2012). The impact of internet pornography on adolescents: A review of the research. 19(1-2), 99-122. doi:10.1080/10720162.2012.660431Copy Koletić G. (2017). Longitudinal associations between the use of sexually explicit material and adolescents' attitudes and behaviors: A narrative review of studies. Journal of adolescence, 57, 119–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2017.04.006Copy
And not only that, research is shedding light on a previously little-known fact about porn: it’s harmful to consumers’ brains. Thanks to all the research that has been done in recent years, people are finally starting to realize how toxic pornography can be.
The research on how porn affects how consumers view themself, their partner, and their relationships, in general, is becoming prevalent. When people consume porn, it not only warps their view of others. It can also twist their view of themselves. Here’s how.
Insecurity and mental health impacts
Studies have found that when people engage in an ongoing pattern of “self-concealment,” which is when they do things they’re not proud of and keep them a secret, it can not only hurt their relationships and leave them feeling lonely but can also make them more vulnerable to mental health issues.Laird, R. D., Marrero, M. D., Melching, J. A., and Kuhn, E. S. (2013). Information Management Strategies in Early Adolescence: Developmental Change in Use and Transactional Associations with Psychological Adjustment. Developmental Psychology, 49(5), 928–937. doi:10.1037/a0028845Copy Luoma, J. B., et. al. (2013). Self-Stigma in Substance Abuse: Development of a New Measure. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 35, 223–234. doi:10.1007/s10862-012-9323-4Copy Rotenberg, K. J., Bharathi, C., Davies, H., and Finch, T. (2013). Bulimic Symptoms and the Social Withdrawal Syndrome. Eating Behaviors, 14, 281–284. doi:10.1016/j.eatbeh.2013.05.003Copy
In fact, a number of peer-reviewed studies have found a link between pornography consumption and mental health outcomes like depression,Harper, C., & Hodgins, D. C. (2016). Examining Correlates of Problematic Internet Pornography Use Among University Students. Journal of behavioral addictions, 5(2), 179–191. https://doi.org/10.1556/2006.5.2016.022Copy anxiety,Wordecha, M., Wilk, M., Kowalewska, E., Skorko, M., Łapiński, A., & Gola, M. (2018). 'Pornographic binges' as a key characteristic of males seeking treatment for compulsive sexual behaviors: Qualitative and quantitative 10-week-long diary assessment. Journal of behavioral addictions, 7(2), 433–444. https://doi.org/10.1556/2006.7.2018.33Copy loneliness,Butler, M. H., Pereyra, S. A., Draper, T. W., Leonhardt, N. D., & Skinner, K. B. (2018). Pornography Use and Loneliness: A Bidirectional Recursive Model and Pilot Investigation. Journal of sex & marital therapy, 44(2), 127–137. https://doi.org/10.1080/0092623X.2017.1321601Copy lower life satisfaction,Willoughby, B. J., Young-Petersen, B., & Leonhardt, N. D. (2018). Exploring trajectories of pornography use through adolescence and emerging adulthood.55(3), 297-309. doi:10.1080/00224499.2017.1368977Copy and poorer self-esteem and overall mental health.Koletić G. (2017). Longitudinal associations between the use of sexually explicit material and adolescents' attitudes and behaviors: A narrative review of studies. Journal of adolescence, 57, 119–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2017.04.006Copy
These studies have found that these links are particularly strong when pornography is consumed to escape negative emotions. They are also strong when pornography consumption becomes heavy and compulsive.Levin, M. E., Lillis, J., & Hayes, S. C. (2012). When is online pornography viewing problematic among college males? Examining the moderating role of experiential avoidance.19(3), 168-180. doi:10.1080/10720162.2012.657150Copy According to another study performed in the United States, researchers found a significant bi-directional association between pornography and loneliness, prompting them to conclude:
“Results revealed that the association between loneliness and viewing pornography was positive and significant…those who viewed pornography were more likely to experience loneliness, and those who were experiencing loneliness were more likely to view pornography. These findings are consistent with research linking pornography use to negative effects.”Butler, M. H., Pereyra, S. A., Draper, T. W., Leonhardt, N. D., & Skinner, K. B. (2018) Pornography Use and Loneliness: A Bidirectional Recursive Model and Pilot Investigation, Journal of Sex & Marital Therapy, 44:2, 127-137, DOI: 10.1080/0092623X.2017.1321601Copy
Although it’s fairly common for consumers to use porn as an escape mechanism or self-soothing technique, research indicates that those who consumed pornography to avoid uncomfortable emotions had some of the lowest reports of emotional and mental well-being.Brown, C. C., Durtschi, J. A., Carroll, J. S., & Willoughby, B. J. (2017). Understanding and predicting classes of college students who use pornography. Computers in Human Behavior, 66, 114-121.Copy Another study examined the relationship between the frequency of online pornography consumption and mental health problems, particularly in the context of “experiential avoidance” or trying to avoid negative emotions. The study found that frequent pornography consumption was significantly related to greater depression, anxiety, and stress. It was also linked to poorer social functioning.Levin, M. E., Lillis, J., & Hayes, S. C. (2012) When is Online Pornography Viewing Problematic Among College Males? Examining the Moderating Role of Experiential Avoidance. Journal Sexual Addiction & Compulsivity: The Journal of Treatment & Prevention, 19 (3), 168-180.Copy
In yet another study, researchers at Columbia University, Yale University, and UCLA found a link between compulsive pornography consumption and poorer mental health. They also found links to low self-esteem and poor attachment in relationships. The authors concluded,
“In this paper, we propose that pornography use has the potential to become addictive and might be conceptualized as a behavioral addiction… individuals who scored higher on the Problematic Pornography Use Scale reported poorer mental health and self-esteem, and more insecure close relationships than those who scored lower, illustrating the negative emotional correlates of problematic pornography use.”Kor, A., Zilcha-Mano, S., Fogel, Y. A., Mikulincer, M., Reid, R. C., & Potenza, M. N. (2014). Psychometric development of the Problematic Pornography Use Scale. Addictive behaviors, 39(5), 861–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2014.01.027Copy
Sex can be great; comparing it to porn isn’t
But your relationship with yourself isn’t the only thing harmed by porn. Your relationship with others can be, too.
To start, dozens of studies have repeatedly shown that porn consumers tend to have lower relationship satisfaction. They also tend to have lower relationship quality.Wright, P. J., Tokunaga, R. S., Kraus, A., & Klann, E. (2017). Pornography consumption and satisfaction: A meta-analysis. Human Communication Research, 43(3), 315-343. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/hcre.12108Copy Perry S. L. (2020). Pornography and Relationship Quality: Establishing the Dominant Pattern by Examining Pornography Use and 31 Measures of Relationship Quality in 30 National Surveys. Archives of sexual behavior, 49(4), 1199–1213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-019-01616-7Copy Perry, S. (2017). Does Viewing Pornography Reduce Marital Quality Over Time? Evidence From Longitudinal Data. Archives Of Sexual Behavior, 46(2), 549-559. Doi: 10.1007/S10508-016-0770-YCopy
Porn consumers tend to experience more negative communication with their partners, feel less dedicated to their relationships, have a more difficult time making adjustments in their relationships, are less sexually satisfied, and commit more infidelity.Maddox, A. M., Rhoades, G. K., & Markman, H. J. (2011). Viewing sexually-explicit materials alone or together: associations with relationship quality. Archives of sexual behavior, 40(2), 441–448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-009-9585-4Copy Research also shows that porn consumers tend to become less committed to their partners,Minarcik, J., Wetterneck, C. T., & Short, M. B. (2016). The Effects Of Sexually Explicit Material Use On Romantic Relationship Dynamics. Journal Of Behavioral Addictions, 5(4) 700-707. Doi: 10.1556/2006.5.2016.078Copy Lambert, N. M., Negash, S., Stillman, T. F., Olmstead, S. B., & Fincham, F. D. (2012). A love that doesn't last: Pornography consumption and weakened commitment to one's romantic partner. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 31(4), 410-438. doi:10.1521/jscp.2012.31.4.410Copy less satisfied in their relationships,Wright, P. J., Tokunaga, R. S., Kraus, A., & Klann, E. (2017). Pornography consumption and satisfaction: A meta-analysis. Human Communication Research, 43(3), 315-343. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/hcre.12108Copy and more accepting of cheating.Rasmussen, K. (2016). A Historical and Empirical Review of Pornography and Romantic Relationships: Implications for Family Researchers. Journal of Family Theory & Review, 8(2), 173-191. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/jftr.12141Copy
Meanwhile, partners of porn consumers also report negative effects, such as lower self-esteem, worse relationship quality, and less sexual satisfaction.Stewart, D. N., & Szymanski, D. M. (2012). Young adult women’s reports of their male romantic partner’s pornography use as a correlate of their self-esteem, relationship quality, and sexual satisfaction. Sex Roles: A Journal of Research, 67(5-6), 257-271. doi:10.1007/s11199-012-0164-0Copy Research also suggests that porn consumption can undermine trust in a relationship and fuel couple conflict.Carroll, J. S., Busby, D. M., Willoughby, B. J., & Brown, C. C. (2017). The porn gap: Differences in men's and women's pornography patterns in couple relationships.16(2), 146-163. doi:10.1080/15332691.2016.1238796Copy
Obviously, relationship problems like these are not new and are not solely caused by porn. Yet, research shows that porn can play a substantial role in fueling these issues. That’s not something that should be ignored.Maddox, A. M., Rhoades, G. K., & Markman, H. J. (2011). Viewing Sexually-Explicit Materials Alone Or Together: Associations With Relationship Quality. Archives Of Sexual Behavior, 40(2), 441-448. Doi:10.1007/S10508-009-9585-4Copy Perry S. L. (2020). Pornography and Relationship Quality: Establishing the Dominant Pattern by Examining Pornography Use and 31 Measures of Relationship Quality in 30 National Surveys. Archives of sexual behavior, 49(4), 1199–1213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-019-01616-7Copy Rasmussen, K. (2016). A historical and empirical review of pornography and romantic relationships: Implications for family researchers. Journal of Family Theory & Review, 8(2), 173-191. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/jftr.12141Copy
Choose love, not porn.
If you have been struggling to quit an unwanted porn habit, please know that you’re not alone. It can feel lonely and frustrating, but there is hope. Research shows that while porn can fuel loneliness, it is possible to overcome a porn habit and its negative effects.Young K. S. (2013). Treatment outcomes using CBT-IA with Internet-addicted patients. Journal of behavioral addictions, 2(4), 209–215. https://doi.org/10.1556/JBA.2.2013.4.3Copy Nathanson, A. (2021). Psychotherapy with young people addicted to internet pornography. Psychoanal.Study Child, 74(1), 160-173. doi:10.1080/00797308.2020.1859286Copy According to one study of individuals trying to quit porn, researchers found that shame predicted increased pornography consumption while guilt predicted sustainable change.Gilliland, R., South, M., Carpenter, B. N., & Hardy, S. A. (2011). The roles of shame and guilt in hypersexual behavior. 18(1), 12-29. doi:10.1080/10720162.2011.551182Copy
So if you’re trying to give up porn to improve your mental health and self-esteem, be kind to yourself. Be patient with your progress. Like anything, it takes time for the brain to recover. However, daily efforts make a big difference in the long run.
Need help?
For those reading this who feel they are struggling with pornography, you are not alone. Check out Fortify, a science-based recovery platform dedicated to helping you find lasting freedom from pornography. Fortify now offers a free experience for both teens and adults. Connect with others, learn about your unwanted porn habit, and track your recovery journey. There is hope—sign up today.
Fight the New Drug may receive financial support from purchases made using affiliate links.
Your Support Matters Now More Than Ever
Most kids today are exposed to porn by the age of 12. By the time they’re teenagers, 75% of boys and 70% of girls have already viewed itRobb, M.B., & Mann, S. (2023). Teens and pornography. San Francisco, CA: Common Sense.Copy —often before they’ve had a single healthy conversation about it.
Even more concerning: over half of boys and nearly 40% of girls believe porn is a realistic depiction of sexMartellozzo, E., Monaghan, A., Adler, J. R., Davidson, J., Leyva, R., & Horvath, M. A. H. (2016). “I wasn’t sure it was normal to watch it”: A quantitative and qualitative examination of the impact of online pornography on the values, attitudes, beliefs and behaviours of children and young people. Middlesex University, NSPCC, & Office of the Children’s Commissioner.Copy . And among teens who have seen porn, more than 79% of teens use it to learn how to have sexRobb, M.B., & Mann, S. (2023). Teens and pornography. San Francisco, CA: Common Sense.Copy . That means millions of young people are getting sex ed from violent, degrading content, which becomes their baseline understanding of intimacy. Out of the most popular porn, 33%-88% of videos contain physical aggression and nonconsensual violence-related themesFritz, N., Malic, V., Paul, B., & Zhou, Y. (2020). A descriptive analysis of the types, targets, and relative frequency of aggression in mainstream pornography. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 49(8), 3041-3053. doi:10.1007/s10508-020-01773-0Copy Bridges et al., 2010, “Aggression and Sexual Behavior in Best-Selling Pornography Videos: A Content Analysis,” Violence Against Women.Copy .
From increasing rates of loneliness, depression, and self-doubt, to distorted views of sex, reduced relationship satisfaction, and riskier sexual behavior among teens, porn is impacting individuals, relationships, and society worldwideFight the New Drug. (2024, May). Get the Facts (Series of web articles). Fight the New Drug.Copy .
This is why Fight the New Drug exists—but we can’t do it without you.
Your donation directly fuels the creation of new educational resources, including our awareness-raising videos, podcasts, research-driven articles, engaging school presentations, and digital tools that reach youth where they are: online and in school. It equips individuals, parents, educators, and youth with trustworthy resources to start the conversation.
Will you join us? We’re grateful for whatever you can give—but a recurring donation makes the biggest difference. Every dollar directly supports our vital work, and every individual we reach decreases sexual exploitation. Let’s fight for real love: